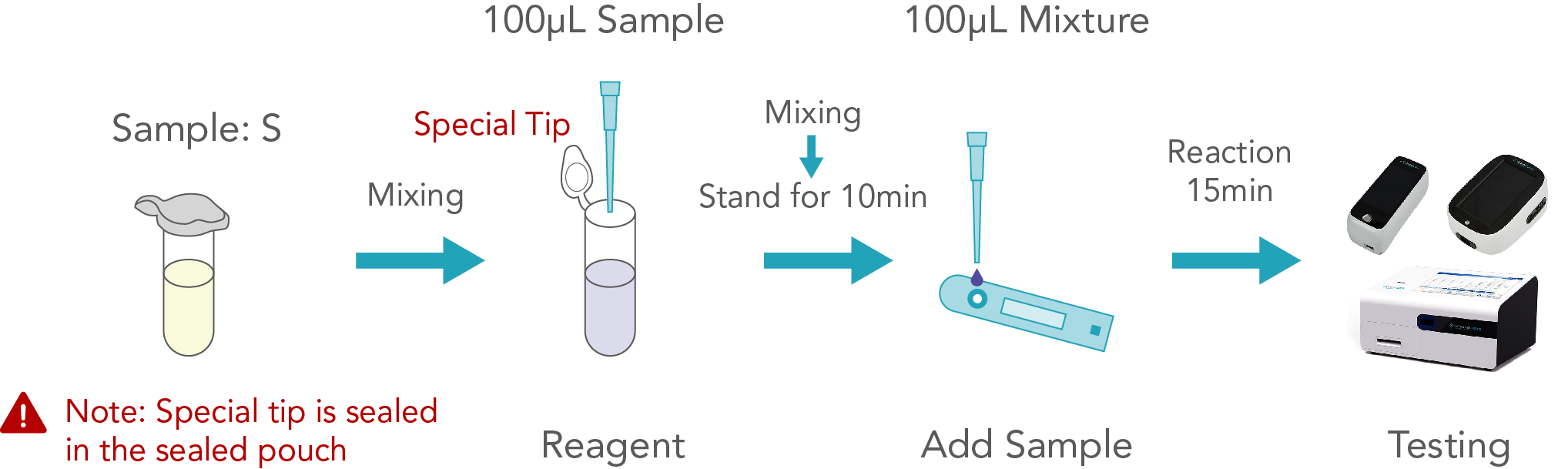
BackDuration: 15 minutes
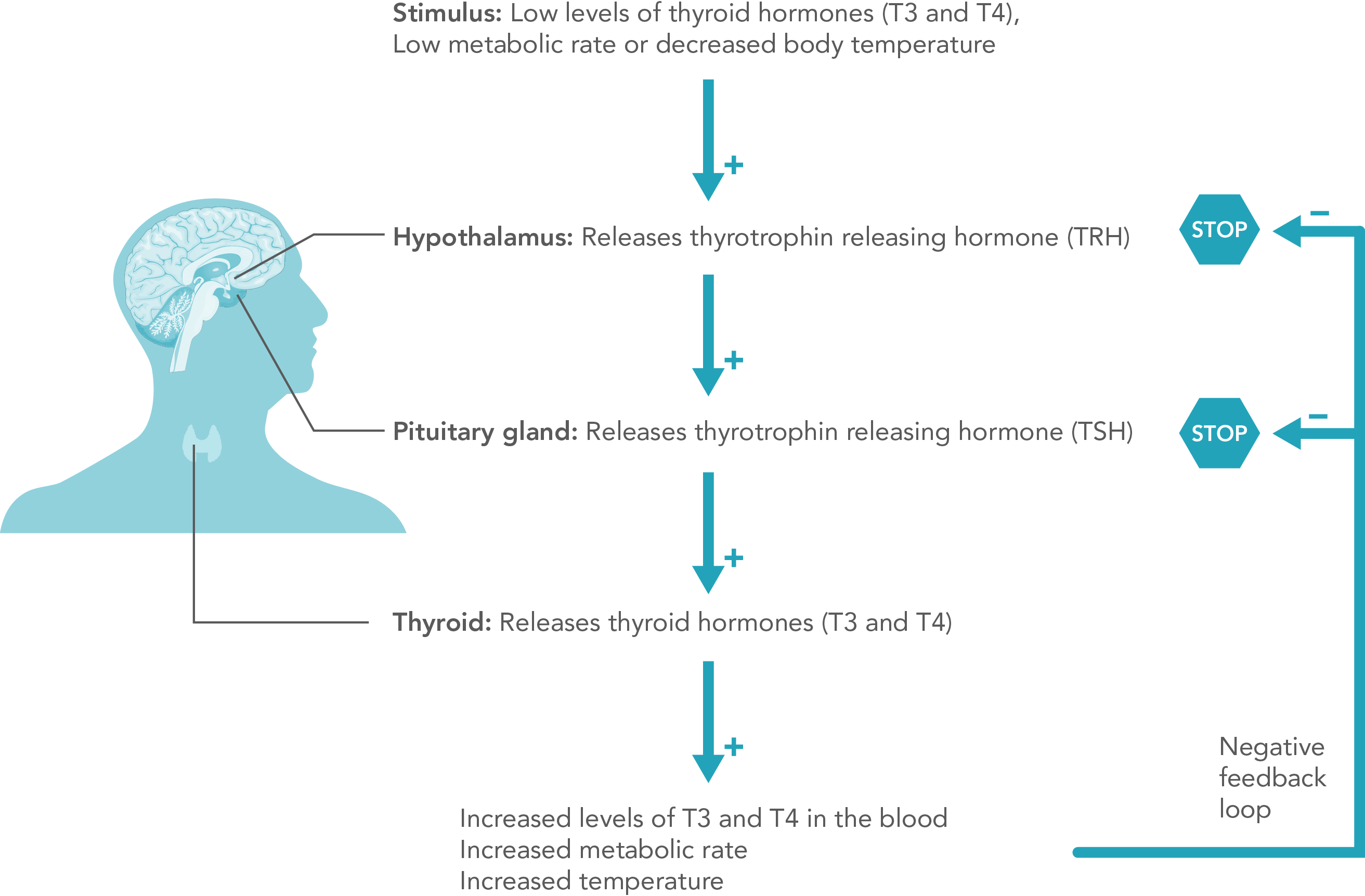
An indicator of thyroid gland function
Clinical significance of test
Total triiodothyronine (TT3) is one of two major hormones made by your thyroid, a small, butterfly-shaped gland located near the throat. The other hormone is called thyroxine (T4.) T3 and T4 work together to regulate how your body uses energy. These hormones also play an important role in controlling your weight, body temperature, muscle strength, and nervous system. TT3 and TT4 are combined tests used to evaluate thyroid function and monitor treatment.
Steps of operation
Clinical application
TT3 increase:
- Toxic diffuse goiter and toxic nodular goiter (Plummer’s disease) include toxic single and multiple nodular goiter, autonomous high functional thyroid nodules or adenomas, hyperthyroidism, hyperthyroid thyroid cancer, etc.
- Serum T3 is the most sensitive index in the diagnosis of hyperthyroidism.
TT3 decrease:
- Hypothyroidism, simple goiter and low T3 syndrome, taking androgen therapy, adrenocortical hormone therapy, nephrotic syndrome, liver failure, drug treatment (such as phenytoin sodium, Baotaisong) and hereditary decrease of thyroid hormone binding protein may reduce serum T3 level.
Interpretation of results
Contact us