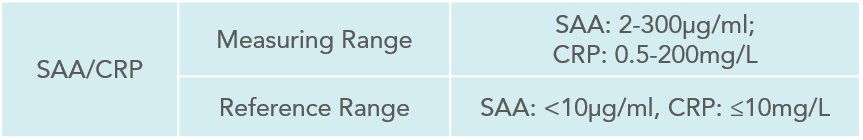
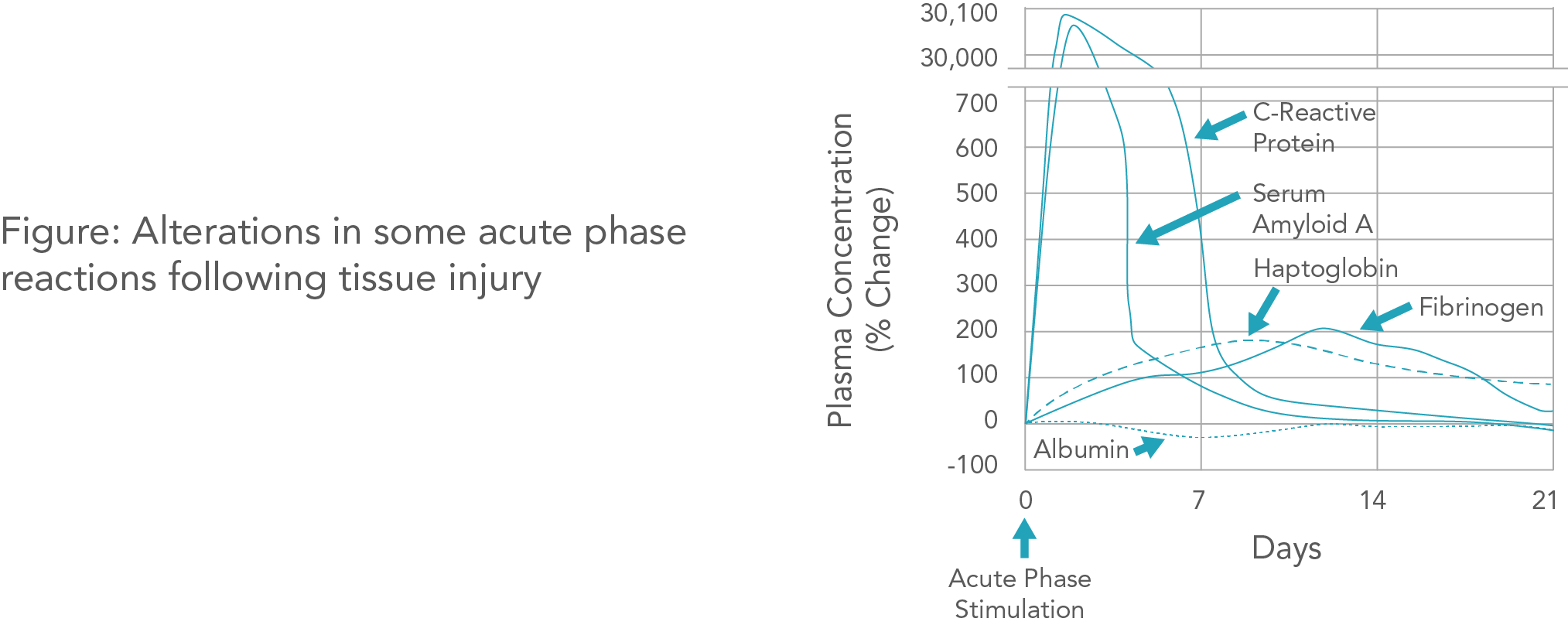
SAA is a sensitive inflammatory marker discovered in recent years. As an acute-phase reactive protein, its concentration increases significantly in acute and chronic inflammatory reactions, reaching more than 1000 times the normal level in 6-8 hours. As SAA has a short half-life, when the body’s inflammatory response is controlled, SAA rapidly drops to the normal level, which makes SAA a sensitive indicator of the body’s inflammatory state such as infection or trauma.
CRP is a typical acute phase protein. It is synthesized by the liver and the epithelial cell in response to infections or tissue damages, and the synthesis is triggered by interleukin-6 (IL-6) and other cytokines produced by macrophages and other white blood cells which are activated in these conditions.