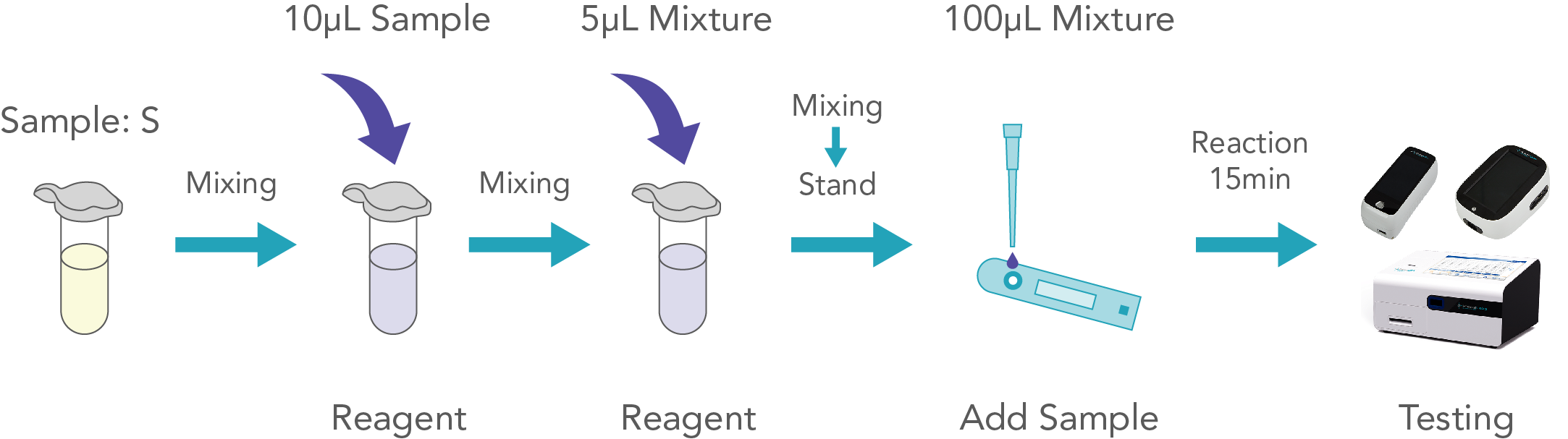
BackDuration: 15 minutes
Reflects immunity and immunoglobulin related diseases
Clinical significance of test
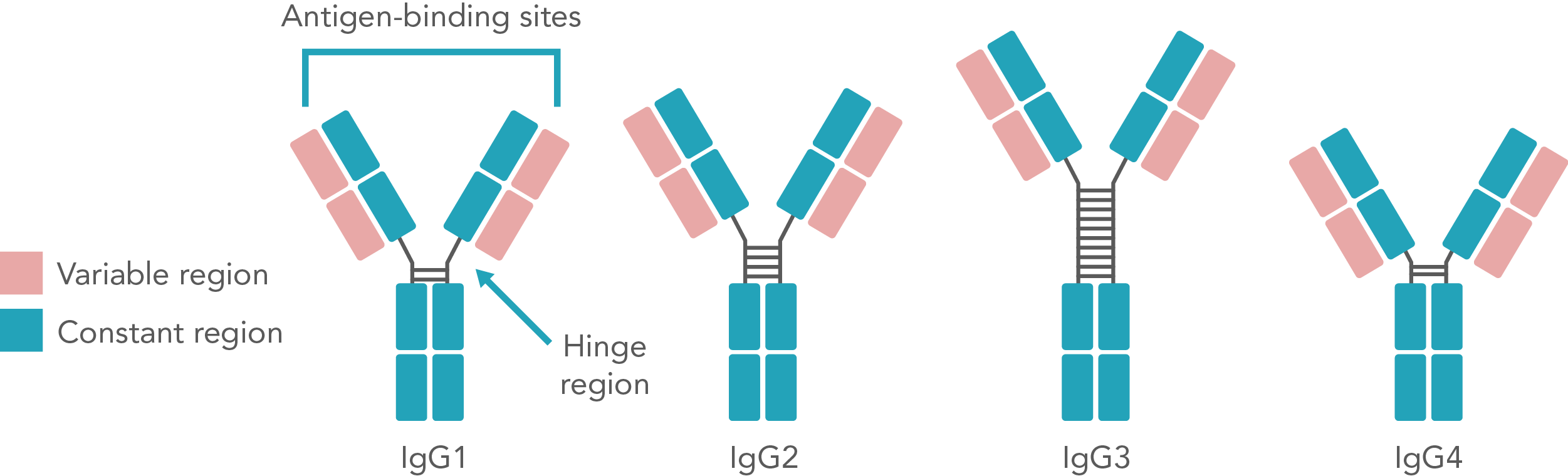
Human immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies consist of four subclasses, immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1), immunoglobulin G2 (IgG2), immunoglobulin G3 (IgG3), and immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4). Structural differences between immunoglobulin G subclasses can be reflected in different biologically important functions, such as antigen recognition, complement activation, and cell surface receptor binding. The determination of human immunoglobulin G subclasses is mainly used clinically for the evaluation of immune function and as an aid in the diagnosis of immune diseases.
Steps of operation
Clinical application
- Frequently used for Immunoglobulin G4-related disease(IgG4-RD) and at one time was considered essential for diagnosis. Increased serum IgG4 levels can support the diagnosis of IgG4-RD in the appropriate clinical context, and the majority of patients (~70%) have increased concentrations.
- However, serum IgG4 concentrations are neither highly specific nor sensitive for IgG4-RD diagnosis. A range of diseases such as biliary tract, pancreatic, liver, and lung diseases also may be attended by increased serum IgG4. )
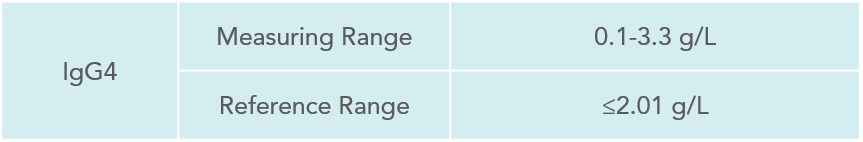
Interpretation of results
Contact us