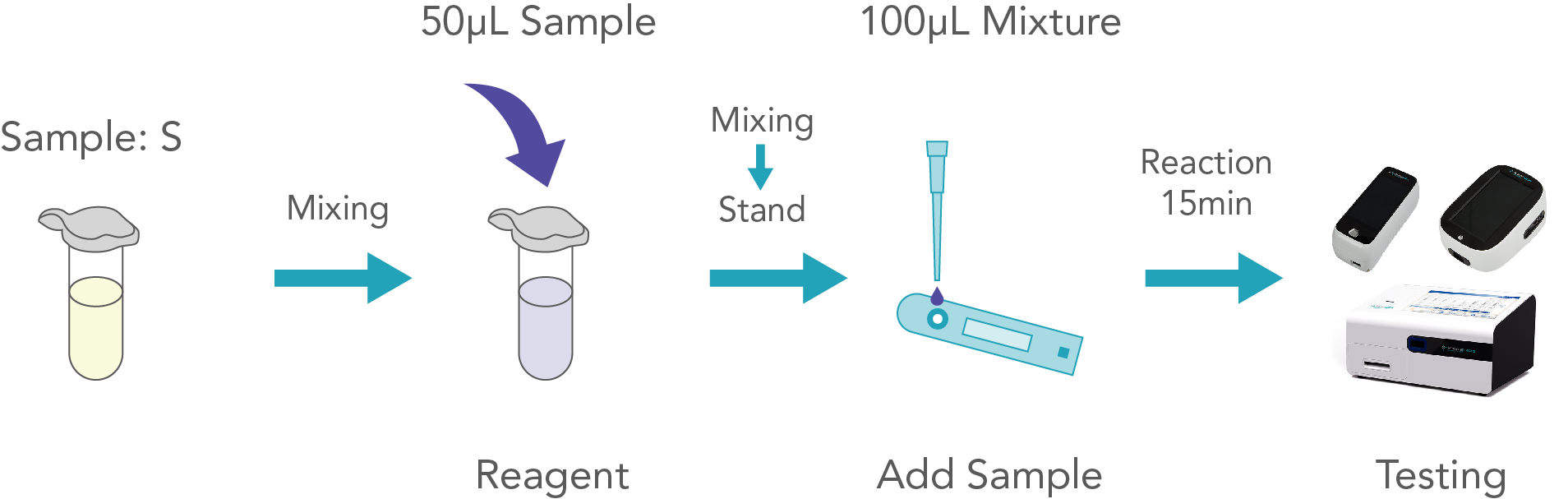
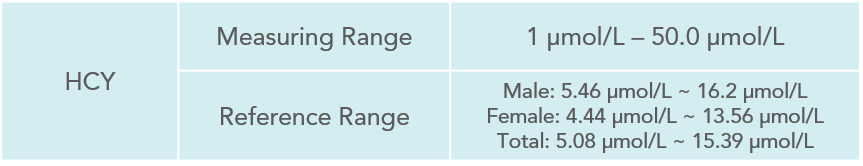
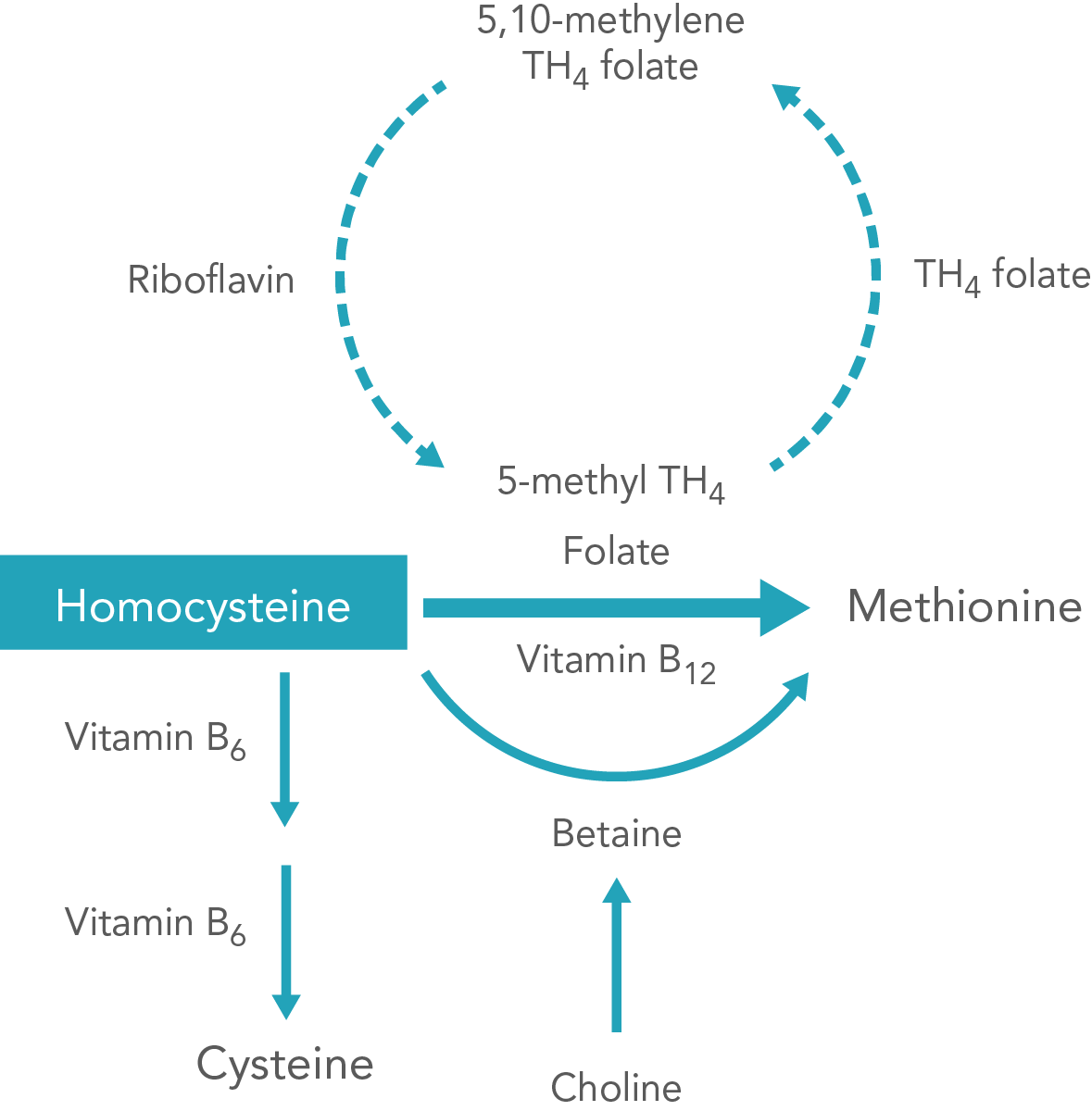
Homocysteine is a produced when methionine is metabolised, and methionine is one of the eleven “essential” amino acids (an essential amino acids must be derived from the diet since the body cannot make them). In healthy cells, homocysteine is quickly converted to other products. About 70% of homocysteine in serum binds to albumin, which is the binding type. The remaining free forms are mainly in the form of disulfide homocysteine and homocysteine-cysteine compounds bound by disulfide bonds, only a small amount of reduced homocysteine is present in serum.