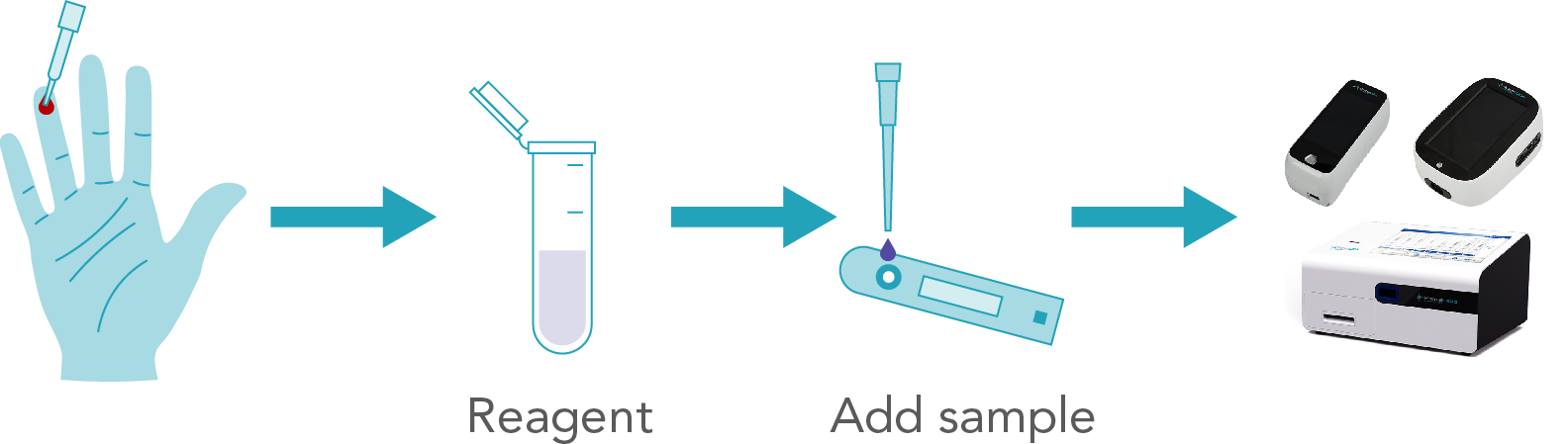
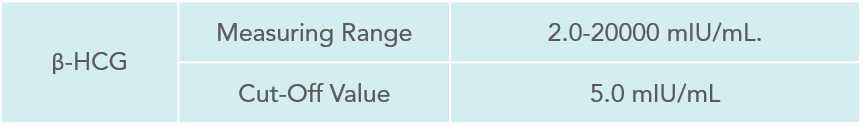
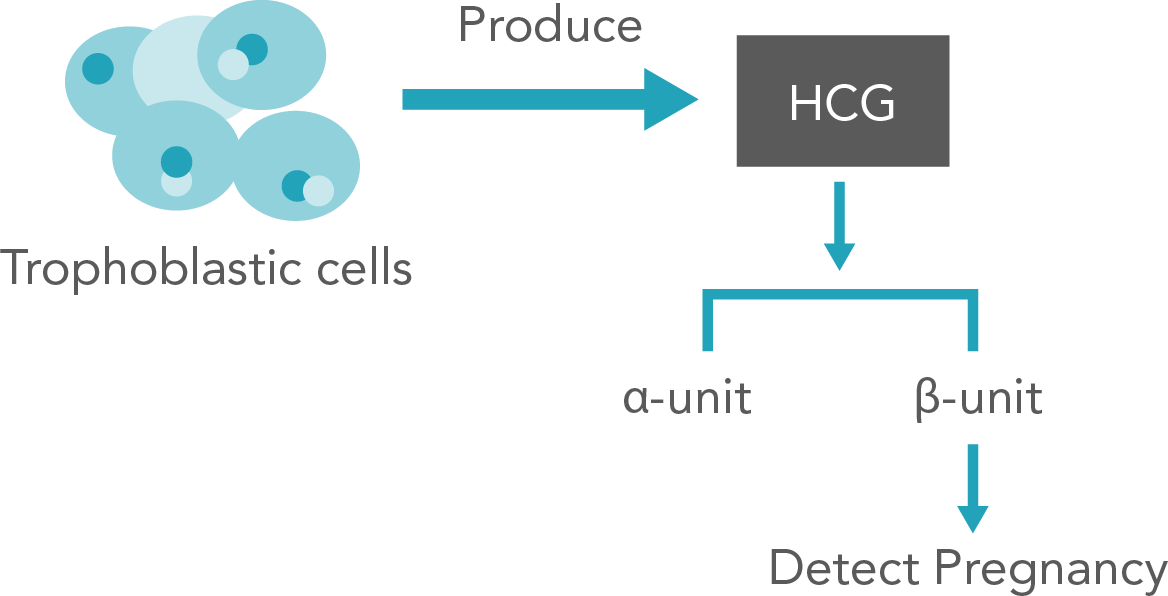
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a proteinaceous hormone produced by the body of a woman after she conceives. It helps to maintain pregnancy until the development of placenta and is mainly secreted in the first trimester. The levels of hCG in blood increase from the 8th day after conceiving and peak during the 10th week. Beta hCG (β-hCG) is a subunit of hCG which can be present in its free form in the serum (the liquid portion of blood).